20天狂宴Pytorch-Day8
低阶 API, 中阶 API, 高阶 API, 登神长阶 API.
低阶 API#
线性回归模型#
生成随机测试数据.
n = 400 |
数据大概长这样.
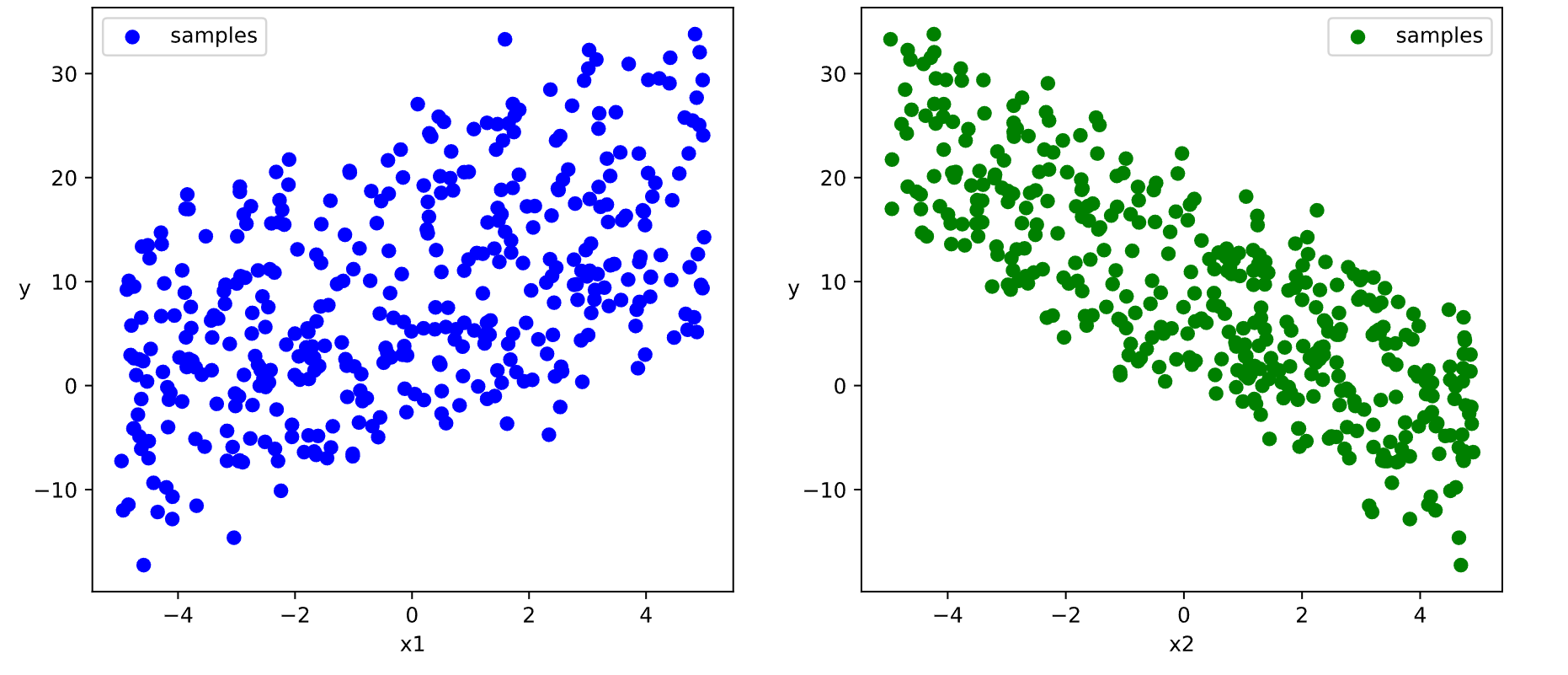
接下来构建数据管道迭代器.
def data_iter(features, labels, batch_size=8): |
接下来定义并训练模型.
class LinearRegression: |
可以用如下代码使用模型并把结果可视化.
plt.figure(figsize = (12,5)) |
DNN 二分类模型#
DNN: 深度神经网络, 二分类: 输出 0 或 1.
同理先生成测试数据, 并构造数据管道迭代器.
n_positive,n_negative = 2000,2000 |
然后定义并训练模型, 使用 nn.Module 组织模型变量.
class DNNModel(nn.Module): |
训练完毕后使用模型.
fig, (ax1,ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1,ncols=2,figsize = (12,5)) |
为啥这节叫 API 啊, 没搞懂啊.
中阶 API#
线性回归模型#
生成数据后构建输入数据管道.
ds = TensorDataset(X,Y) |
定义模型.
model = nn.Linear(2,1) # 线性层 |
训练模型.
def train_step(model, features, labels): |
使用模型并可视化.
w,b = model.state_dict()["weight"],model.state_dict()["bias"] |
DNN 二分类模型#
# 构建输入数据管道 |
现在我知道为什么叫 API 了.
高阶 API#
Pytorch 没有官方的高阶 API, 一般需要用户自己实现训练, 验证和预测循环. 作者仿照 keras 的功能对 Pytorch 的 nn.Module 进行了封装, 设计了 torchkeras.KerasModule 类, 实现了 fit, evaluate 等方法, 相当于用户自定义高阶 API.
线性回归模型#
# 构建输入数据管道 |
倒是没出什么问题, 但是训练速度明显慢了很多, 跑了差不多五分钟, 可能是我没开 GPU 导致的.
# 评估模型 |
DNN 二分类模型#
ds = TensorDataset(X,Y) |
也是速度明显变慢, 不太清楚具体为什么和之前差这么多.